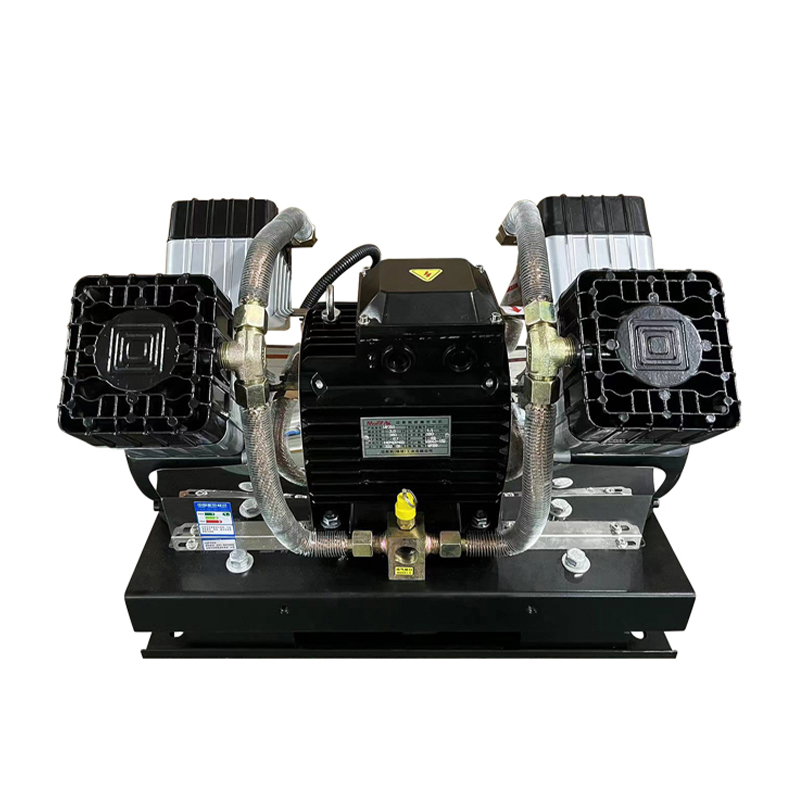
The application of air compressors in laboratories and scientific research institutions is mainly reflected in providing stable gas pressure and flow to ensure the accuracy and smooth progress of experiments.
The application of air compressors in laboratories is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Chemical experiments: In chemical experiments, air compressors meet experimental needs by providing stable gas pressure and flow. For example, in catalytic reactions, air compressors ensure that gases can be stably transported to the reactor to ensure the smooth progress of reactions; in gas analysis and detection, air compressors provide stable gas flow to ensure the accuracy of measurement results.
2. Physical experiments: In physical experiments, air compressors simulate gas behavior in real scenes by generating high-pressure gas, providing support for research in gas mechanics, fluid mechanics, and other fields. At the same time, in the drive and operation of precision instruments, air compressors provide stable gas flow and pressure to ensure the accuracy of experimental results.
3. Biological experiments: In biological research, air compressors provide a reliable gas supply to ensure the normal progress of biological experiments. For example, in the process of cell culture, the air compressor provides a stable gas environment to ensure the normal growth and physiological function of cells; in experiments such as PCR reactions, the air compressor provides a stable gas supply to ensure the accuracy of experimental results.
In addition, the application of air compressors is not limited to laboratory environments but also includes pneumatic tools, instrument control and automation devices, food and pharmaceutical industries, wind tunnel experiments, metal smelting, coating sandblasting, and other fields.
In summary, air compressors play an indispensable role in laboratories and scientific research institutions, providing stable gas pressure and flow to ensure the accuracy and smooth progress of experiments.
















 IPv6 network supported.
IPv6 network supported.
